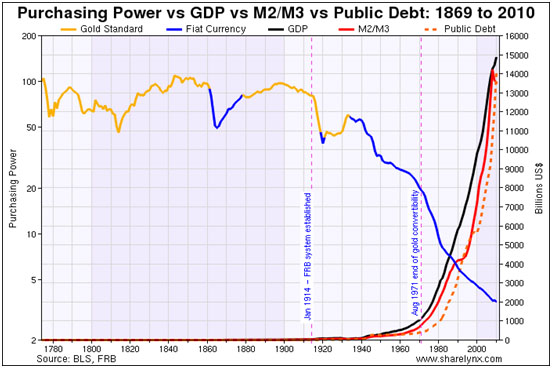
Richard Karn: It's interesting that if you go back to the late 18th century, the dollar has been on the gold standard roughly the same amount of time it has been on the Federal Reserve System, which presents us with a wonderful opportunity to compare the dollar's purchasing power over time.
Throughout the 19th century with all of the booms and busts, the wars, and the incredible territorial and industrial expansions, the dollar maintained its purchasing power very well on the gold standard. Since 1914, when the U.S. went to the Federal Reserve System and especially since it has become a purely fiat currency system since closing the gold window in 1971, the dollar's purchasing power has collapsed. Under the Fed's administration, the dollar has lost well over 95% of its purchasing power.
We show this chart in our presentations, pointing out that the purchasing power of the dollar on the left scale is in log format while the GDP, M2/M3 and Public Debt figures are in linear format on the right scale. Our intention here is simply to highlight the explosion of nominal GDP, M2/M3 and Public Debt corresponds with the collapse of the real purchasing power of the dollar that attended the end of any pretense to adhering to a gold standard in 1971.
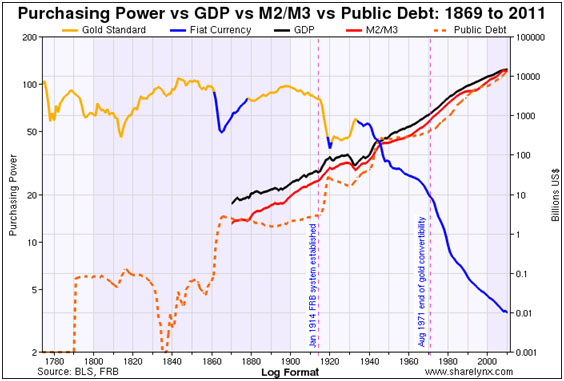
However, in order to dispel any accusations of bias, here is the same data in log format on both scales: the take-away is still that the explosion of nominal GDP, M2/M3 and Public Debt corresponds with the collapse of the real purchasing power of the dollar that attended the end of any pretense to adhering to a gold standard. If anything, to mathematicians the chart is even more damning.
While public awareness of this problem has grown steadily for 40 years, grassroots objection is just now reaching a critical mass, especially among the younger followers of presidential candidate Ron Paul. That is why Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke, in reaching out to the next generation of leaders with his series of university lectures, is disingenuously making a point of damning the gold standard for its "volatility" while utterly dismissing the simple truth that at least on the gold standard the dollar retained its purchasing power over time, something the U.S. dollar under the Federal Reserve Bank's stewardship unequivocally has failed to do.
In 1914, the U.S. moved away from the gold standard and into a financial system based on debt and ever-increasing monetary inflation; the transition was completed in August 1971 when Nixon ended dollar convertibility into gold, and John Connelly famously told concerned European bankers, "it's our currency, but it's your problem."
What has emerged is a system under which people earn more nominal dollars of less real value, which disguises the loss of real purchasing power. For four decades, real wages have not kept up with the rate of inflation. Savings have been drawn down and the standard of living in the U.S. has declined. As a consequence, debt levels have soared.
The Fed is targeting inflation rates of 2% to 3% per year, which roughly equates to the inflation rate Americans experienced under the gold standard over the entirety of the ninteenth century. We have long suspected that this figure was chosen because the Fed believes that is the threshold people will tolerate being stolen from their paychecks without complaint. But 2% to 3% inflation compounded annually over the course of a 35- or 40-year working career amounts to a massive loss of purchasing power as well as fostering a false sense of security regarding one's financial situation.
This is a very sophisticated swindle, and all of the powers of government are being brought to bear in order to hide what they have done or to deflect blame, but they are increasingly being cornered by demographics. For most of their working careers, people are too busy earning a living and raising a family to take the time to monitor what monetary policy was doing to their life savings and the retirement they envisioned that they can no longer afford.
TGR: And now the largest wave of retirees in American history is about to have a nasty suprise?
RK: Exactly. Retiring Baby Boomers are discovering they have been duped and that their golden years have been confiscated by a government they believed was serving their interests—and this largest cohort of the population, as well as an increasing number of young people facing a very bleak future determined for them before they were born by deficit spending politicians and their social welfare programs that have simply run amok—are saying "We're mad as hell, and we're not going to take it anymore."
I believe that when you see the radical left in America as manifested by the Occupy Wall Street movement marching right by the radical right in America as manifested by the Tea Party movement effectively mouthing the same slogans, and seeing their ranks swell with retiring Baby Boomers, change is at hand.
The United States has a history of reform, of "throwing the bums out," and we think it likely that time is at hand once again.
To be clear: we think this is a good thing, a cleansing thing, that will lead to better lives for the mass of Americans.
TGR: You dubbed the destructive course of fiat currencies and sovereign debt levels the "global pandemic of corruption" and suggested that if people want to grow wealth in a negative real-interest-rate environment they must speculate. But where?
RK: In a negative real-interest-rate environment, if you do nothing, you lose money because the purchasing power of your money is in perpetual decline. But where should you invest? At The Emerging Trends Report, we are students of history, and what is transpiring today is not new—in fact, it has happened hundreds of times before, just not on a global scale. History tells us there has never been a successful fiat currency—every single one has failed for exactly the reasons we are experiencing firsthand today. Over time, a fiat currency's purchasing power is utterly destroyed by politicians. So obviously, we like gold and silver, which we will come back to in a moment.
Under a fiat currency regime, the rubber always meets the road at real assets, particularly resources, which simply cannot be conjured with the stroke of a few computer keys.
First, we like oil and gas. If there are two aspects of the U.S. economy that still represent American innovation and entrepreneurial spirit, it is technology and the oil and gas industry, the latter of which is frequently overlooked as a technology play. America does oil and gas better than anybody else. Having natural gas at $2.50 per million BTUs may be the most important competitive advantage America has been legitimately afforded since World War II. It would be foolish not to take advantage of it, and we think the market will overcome the array of bureaucracies aligned against it.
Second, we like large, job-generating, economy-enhancing infrastructure projects, in particular oil and gas pipelines, the rebuilding of the North American electrical grid, and water and wastewater treatment plants—as well as the engineering and construction firms that will make it happen.
American politicians of all political stripes have neglected the maintenance, replacement and expansion of U.S. infrastructure for the better part of 30 years, preferring to kick the infrastructure can down the road while promoting pet vote-buying projects, but we have reached a point where that is no longer possible—we've run out of road. We have gas lines exploding, massive sink holes or subsidence from water main leakage, and a rapidly increasing incidence of brown- and black-outs.
This infrastructure program will drive the third and most speculative theme: specialty metals, all of which are leveraged either to technological advance, or the base metals upon which a domestic infrastructure rebuild program will rely.
When the U.S. goes into the market for the materials to undertake this rebuild cycle, prices will take off because there is far less of these specialty metals available today than people realize, and they are harder and more expensive to extract, process and bring to market. The upside on these metals is truly stunning.
And of course, we like gold and silver—the ultimate anti-fiat currency.
TGR: You've spent a lot of time in Australia looking at precious and specialty metal projects. Tell us: the success of the Australian mining industry has helped raise the Australian dollar against the U.S. dollar. What effect is that having on the mining sector?
RK: First and foremost, it is undercutting the mining industry's profitability. Because gold and silver are priced in U.S. dollars, the Australian dollar, in which they incur operating expenses, is going up against the U.S. dollar, despite various
hedging strategies, profitability has not matched the increase in the price of gold or silver.
People in North America do not realize how difficult it is for small Australian companies to get financing. As a result, companies fund themselves by issuing shares. North American investors see an Australian company with half a billion shares out there, selling at $0.09, and they assume this is bad management, when in reality equity dilution is often a matter of not having another course available to them.
In response to the prolonged dearth of financing, which actually predates the global financial crisis, we are starting to see more medium and large companies buying smaller companies with good deposits with equity, or company scrip—the corporate equivalent of fiat currency. I believe we will see an acceleration in this trend over the next 18 months with premiums ranging from 30% to 70%.
The problem for the acquiring medium and large companies will be how much equity dilution their shareholders will tolerate before there is a backlash.
TGR: Do you particularly like gold companies in this regard?
RK: Absolutely. This trend is especially prevalent in the Australian gold sector.
TGR: Have there been any recent discoveries in Australia that have investors and the mining sector excited?
RK: I'd say over the course of the last year Northern Star Resources Ltd. (NST:AUX) and Gold Road Resources Ltd. (GOR:ASX) have probably caused the most excitement. We plan to visit both soon. Gold Road has what may prove to be a whole new gold region called the Yamarna Belt, north of the Tropicana project in Western Australia. We also want to take a look at Silver Lake Resources Ltd. (SLR:TSX), Ramelius Resources Ltd. (RMS:ASX), which is the highest grade gold mine in Australia, Alacer Gold Corp. (ASR:TSX), and dozens of others.
In fact, we'll be spending the majority of the next 18 months in Western Australia to do exactly that.
TGR: Your newsletter has a bias for historic gold producers. Can you give us some names?
RK: I'll give you two with interesting stories. The first is Morning Star Gold NL (MCO:ASX), a narrow vein gold mine at Woods Point in Victoria. Western Mining ran it for 25 years, and took out 25,000 to 28,000 tons of ore each year, grading 27 grams of gold per ton (g/t). Then it stopped production, not because the grade was declining or they were running out of ore but because the fixed price of gold was undermining profitability, and management decided to go chase nickel during the Poseidon Boom in the 1960s—they simply closed all six of their eastern gold mines.
After overcoming a host of obstacles, management has been very good at communicating with shareholders on its website. Morning Star has finally concluded the majority of its capital spend and has brought the mine back into production—albeit more slowly than anticipated. It has a 900,000-ounce (oz) resource with considerable exploration upside.
It's been a "hard slog" for the Morningstar crew, but things are finally coming together. It is building toward production on multiple fronts and drilling on a couple of new reefs. One interesting anomaly Morningstar is experiencing as it resumes production is that it is finding that the final ore grade reconciliations differ from the on-site estimations, often coming in 2–4 times higher, which is consistent with historic production and should be reassuring for shareholders.
While the Morning Star mine itself will be profitable, I think the upside for shareholders will be found in the myriad historic sites spread over its 200 square kilometers of tenements in the Woods Points region. Historically, mining operations throughout the Jamieson-Walhalla Synclinorium lacked the capital to operate below the weathered zone of the countless dykes in the region. Of the hundreds of mines that were sunk in the region, only three raised sufficient capital to go below the water table with mechanization. So Morningstar has all of these targets where gold was found and extracted, but only very superficially, which we think presents a remarkable opportunity.
TGR: What are the cash cost projections?
RK: I think the company is using $750/oz all-in cash costs.
TGR: Do you think that is on the high side?
RK: No. There is a lot of fancy footwork being employed in annual reports in the gold sector. When I say all-in costs, I mean everything, including administration and exploration. I wouldn't be surprised if the all-in cost of gold production industry-wide right now is really in the vicinity of $1,000/oz.
TGR: And the second name?
RK: Cortona Resources Ltd. (CRC:ASX), which is developing Dargues Reef, located about 60 kilometers (km) east of Canberra, the Australian capital. The large tenement package Cortona controls encompasses the majority of the sites of the biggest gold rush in New South Wales history, during which miners recovered 1.2 million ounces (Moz) of alluvial gold.
Dargues Reef may be the source, or one of the sources, of all that alluvial gold, the literal motherlode, but because of the remoteness at the time and the processing technology of the day, old-timers were unable to mine Dargues Reef economically.
Cortona has come up with a very good, and very unusual resource, in that it has an unusual uniformity grade of 7.4 g/t. To date, Cortona has also found two other geological formations exactly like Dargues Reef, which may create tremendous upside.
This is the first new gold mine to be permited in New South Wales in more than seven years and represents no mean feat. Cortona's management has been actively engaged with the community and environmental groups for a number of years, and I think they really should be applauded for their efforts. If Cortona finds the source of that 1.2 Moz of alluvial gold, it will be opening up a new gold field in New South Wales of all places, one of the more populated areas in Australia.
TGR: Do you expect issues with permitting a bigger operation?
RK: One of the "nice" things, from an environmental point of view, about an underground narrow vein operation is that it has a very small environmental footprint. In the case of Dargues Reef, about half of the gold will be recovered by simple, unthreatening gravity separation, and the remaining concentrate will be trucked to a carbon in leach (CIL) plant 400km away.
TGR: Do you have any parting thoughts on precious metals in Australia?
RK: Australia is a safe country. It has very good miners and very good geology. We see an absolute wall of money headed Australia's way at some point because the worse the sovereign debt and sovereign risk issues get, the more people will pay a premium for safe countries in which to operate. That pretty much sums it up.
TGR: Richard, thank you for your time.
RK: It's been a pleasure.
Richard Karn, managing editor of The Emerging Trends Report, has a broad, multi-disciplinary background, industry contacts, and a working knowledge of these metals as well as considerable research, analytical and writing experience pertaining to them. His firm has published nine Emerging Trends Reports, which were updated in the aftermath of the global financial crisis and published in the form of an eBook, Credit & Credibility. For more than two years The Emerging Trends Report has been conducting a boots-on-the-ground survey of Australian precious and specialty metal projects. If you would be interested in participating in the exciting venture, please contact Karn at [email protected].
Want to read more exclusive Gold Report interviews like this? Sign up for our free e-newsletter, and you'll learn when new articles have been published. To see a list of recent interviews with industry analysts and commentators, visit our Exclusive Interviews page.
DISCLOSURE:
1) Brian Sylvester of The Gold Report conducted this interview. He personally and/or his family own shares of the following companies mentioned in this interview: None.
2) The following companies mentioned in the interview are sponsors of The Gold Report: Morning Star Gold NL. Streetwise Reports does not accept stock in exchange for services.
3) Richard Karn: I personally and/or my family own shares of the following companies mentioned in this interview: Morning Star Gold NL, Cortona Resources Ltd. I personally and/or my family am paid by the following companies mentioned in this interview: None. I was not paid by Streetwise Reports for participating in this story.