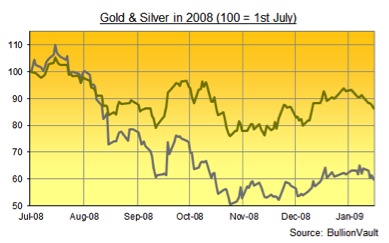
People think the gold price always goes up in a crisis, right until they find out it doesn't. And the reason that this now feels so much like the Lehmans collapse of three years ago is that, looking at the numbers alone, you'd think it was autumn 2008.
Put silver to one side. Because with 60% of annual demand going to industry, the restless metal remains very exposed to the global economic downturn. Whereas gold, long term, tends to rise when other investments—shares, bonds, cash, real estate—fail to deliver.
Look at the grinding losses of Treasury-bond or equity holders in the late 1970s, or the Tech Stock slump of 10 years ago, or the sub-zero real returns paid to cash savers—across the world, after inflation—over the last half-decade.
By the same token, gold tends to fall when investors can see better opportunities elsewhere. Short-term U.S. deposit rates of 19%, for instance, paid above-inflation returns of nearly 10% in 1980. Little wonder the gold price sank from its then-record peak of $850 an ounce, and kept sinking as U.S. bonds paid an average 4% real interest rate for the next 20 years.
Whereas today? Thanks to Operation Twist already snarling everything up, 30-year U.S. Treasury bonds now offer just 2.79% to hungry new buyers. By the time they mature in 2041, Washington's debt-to-GDP ratio will stand around 400% according to one credible estimate—a mere 2.5 times the burden about to force Greece's default—with debt-interest alone eating more than $1 in every $4 generated by what is very unlikely to remain the world's single largest economy.
In return for taking that risk, 30-year bondholders will meantime earn one full percentage point less than inflation this year. Gotta get some for your portfolio, right?
Or take the Japanese yen—the world's other ugliest currency. Like the dollar, it's managed by central bankers so bent on printing money to "fix" every problem they spy, capital markets now have a nervous breakdown each time they don't. Nor do the dollar or yen pay their domestic cash savers anything, while foreign investors have seized the chance to borrow both at next-to-nothing, using the money to buy more exciting assets, such as slow-drying paint (and non-rusting gold) through to Brazilian Reals (down 11% so far this week versus the yen) or wheat (down 5% against the dollar on Thursday alone).
The financial world cannot bear it when the dollar or yen go up. Which is just what they're doing, thanks to the interbank lending crisis—otherwise known as the latest credit crunch—forcing dollar and yen debtors to pay back all those "free" dollars and yen used to finance investments in stocks, bonds and commodities.
The "liquidity line" pumped into Europe by the Federal Reserve last week proves just how desperate eurozone banks have become. So too does the rise of the gold offer rate—the rate of interest offered by bullion owners, through London's wholesale market, who want to borrow cash and put up their gold as collateral. Yes, holding gold is great, but holding cash is better still—short term—when your institution can't otherwise raise a loan in the market, or needs to pay back its dollar or yen financing.
Those two currencies, source of so much free investment cash over the last decade, really are at the heart of this current slump. This week so far, for instance. . .
- Japanese yen price of gold: down 5.1% from the weekend
- U.S. dollar gold price: down 4.5%
- Euro (and Swiss franc) price: down 2.2%
- Pound sterling price: down 1.9%
- Canadian dollar price: up 1.4%
- Aussie gold price: up 2.2%
See what's happened to gold versus the commodity currencies? Issued by resource-rich states, the money of Australia or Canada look a no-brainer when base metals and energy prices rise. But when copper drops 30% in a month? Or crude oil sinks so fast that the Opec cartel threatens to tighten supply for the first time since—oh!—crude oil last sank this fast?
Just as no one cared when commodities rose that the Canadian dollar paid way less than Canadian inflation, so no one cares today that the Aussie currently pays 4.5% more per year than it should cost to borrow and sell U.S. dollars. Because no one can borrow dollars, not in Europe especially. The warning was there, however, just as it was in mid-2008 when the first slug of the crisis neared its peak. The gold price in terms of both Australian and Canadian dollars rose to new record highs as the U.S. gold price sank in late 2008. It hit new record highs again in August and Sept. this year against both commodity currencies—a signal that gold's new high in the U.S. dollar was flashing "credit deflation!" instead of the consumer-price inflation most economists still think gold requires to go higher.
Yes, today is just as much about investors selling gold to cover losses elsewhere as it is about the liquidity crisis forcing dollars and yen higher. But again, that's just like Lehmans' collapse. And just like that slump, it's hard to see today's drop as the end of gold's multi-year bull market. Because everything else looks just as bad as it did yesterday. Only worse.
Can't speak for silver, though. Yes, it typically moves in the same direction as gold day to day. Yes, a bull market in one is inconceivable without a rise in the other. But over the last 43 years, silver has moved 1.7% for every 1% move in gold on average, both up and down. Whereas the huge run-up this spring, plus the dramatic pull-back since then, mean silver has so far in 2011 moved 2.9% for every 1% move in gold, magnifying the yellow metal's rate of change almost three-fold.
So far this week, silver has lost 10.1% versus the dollar and more than 11% versus the yen. It's even lost ground to the Aussie and Canadian dollars. But that's the trouble with a financial crash. Even the smart people—the people who saw it coming, and might even be right in the long run—get whacked just like everyone else.
Adrian Ash
BullionVault
Gold price chart, no delay | Buy gold online at live prices
Formerly City correspondent for The Daily Reckoning in London and head of editorial at the UK's leading financial advisory for private investors, Adrian Ash is head of research at BullionVault—winner of the Queen's Award for Enterprise Innovation, 2009 and now backed by the World Gold Council market-development and research body—where you can buy gold today vaulted in Zurich on $3 spreads and 0.8% dealing fees.
(c) BullionVault 2011
Please Note: This article is to inform your thinking, not lead it. Only you can decide the best place for your money, and any decision you make will put your money at risk. Information or data included here may have already been overtaken by events—and must be verified elsewhere—should you choose to act on it.