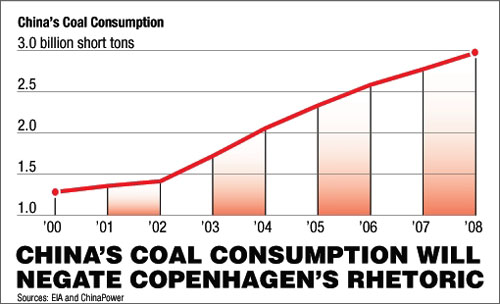
While political leaders and environmental activists are gathered in Copenhagen to talk about carbon footprints, cap-and-trade schemes and a "carbon-constrained world," China continues burning coal at record rates. And that coal consumption means that all of the rhetoric in Copenhagen will largely amount to nothing.
In 2008, China consumed close to 3 billion tons of coal—more than twice that consumed in the U.S., and about 40% of the world consumption that year. From 2000 to 2008, China's coal use jumped by 232% and coal-fired power generation capacity increased by 265%. During that time, coal's share of China's power-generation mix has stayed at about 75%. In 2008, coal provided about 600 gigawatts of power capacity. Of the remaining 193 GW, the vast majority, about 170 GW, was provided by hydroelectric facilities.
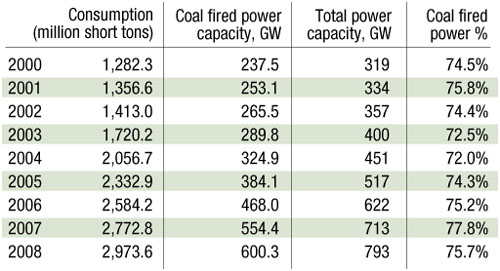
Sources: EIA and ChinaPower
According to a recent report by China's powerful National Development and Reform Commission, the country has been increasing its coal-fired generation capacity at a rapid rate, bringing online more than one power plant per week, adding to capacity while replacing less efficient, smaller power plants. With such huge increases in capacity, China will likely be a net coal importer in 2009 for the first time, according to the NDRC estimates. Given coal's dominant position in China's electric sector, there's no doubt that for the next 50 years or so, coal-fired power plants will continue to be major players in the country's generation mix.
Although unable to reduce coal consumption, China is working to reduce pollution from the coal plants and improve their efficiency. About 50GW of small (100 megawatts or less) and inefficient coal-fired power plants in the eastern part of the country were scheduled to be shut down from 2006 to 2010. So far about 90% of this goal has been met.
During the last two years, China has surpassed the United States to become the largest carbon dioxide emitter and about 80% of China's carbon dioxide emissions come from burning coal. Over 50% of China's coal consumption is used for electricity generation (the rest is used for industrial fuel and chemical feedstock), and over 70% of the electricity is used for industrial production.